Isola P, Zhu J Y, Zhou T, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2017: 1125-1134.
本篇论文提出conditionnal GAN (supervised)结构
- 学习input image到output image之间的映射。
- 学习特定的loss function用于训练映射,即单独使用L1 loss (或L2 loss)会产生blur现象,而再此基础上进一步使用adversarial loss能够学习到适合特定数据集的loss function, 从而sharpen生成的图像 (判别器D能够判断blurry image为fake)。
因此,针对不同任务 (Figure 1),该方法具有通用性。

1. Contribution
- 针对不同任务,cGAN具有通用性。
- Achieve good result, 并分析cGAN结构中的一些重要部分
2. Relative Work
2.1. Loss类型
- Structured loss 每个像素点独立考虑. per-pixel classification loss, regression.
- Unstructured loss penalize the joint configuration of the output, 如conditional random fields. cGAN的unstructured loss是学习到的。
2.2. cGAN
- 前人也apply GANs in conditional seting, 但是针对特定应用的,而本论文的cGAN提出的是通用框架。
- 本论文的cGAN使用到了U-Net和PatchGAN.
3. Objective
- GAN
- z->G->y
- y->D->true or fake

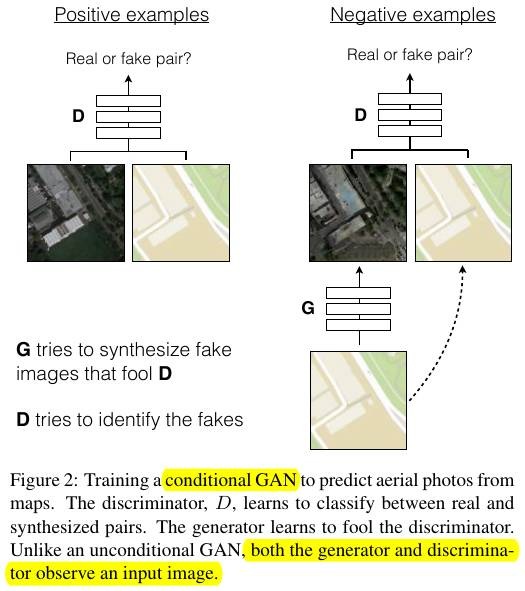
- cGAN (Figure 2)
- {x, z}->G->y
- {x, y}->D->true or fake

- 使用L2会产生更严重的blur.

- 最终的目标函数
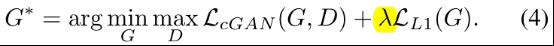
- 没有噪声z的网络会产生一个特定的输出,无法match any distribution, 因此cGAN加入噪声z,但在本篇论文实验中发现,G能够学习到如何ignore 噪声,从而在模型的test阶段也使用dropout产生noise.
4. Network architectures
4.1. Skip connection of G
- 在auto-encoder结构中,input的所有信息会在所有layers传输。为了避免这种方法,在AE的基础上添加skip connection, 即U-Net (Figure 3).

4.2. Markovian D (PatchGAN)
- L1 loss和L2 loss能够capture low frequencies, 因此需要约束D能够capture high frequency structure,即PatchGAN (N X N patches). D effectively models the image as a Markov random field.
4.3. Optimization and inference
- 在test阶段,使用dropout, BN使用 the statistics of the test batch, rather than aggregated statistics of the training batch.
- instance normalization在图像生成任务上很有效。(batch size为1,使用the statistics of the test batch)
5. Experiments
- L1产生blur.
- cGAN sharp imaged,但是存在artifacts.

- (Table 1) cGAN优于GAN,加上L1 loss后,cGAN也相对较优。

- Colorfulness
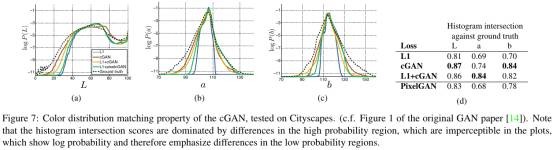
当不确定edge的位置时,L1会产生blur和averrage ( L1 will be minimized by choosing the median of of the conditional probability density function over possible colors.) 从而导致narrower distribution than the ground truth (Figure 7).
- Analysis of the G (Figure5)

- Analysis of the D (Figure 6, Table 2)
- Pixel GAN output 1x1 of D.
- Image GAN output 256x256(full image size) D.
- Patch GAN output 70x70(在本实验中) D.
- Fully-convolutional translation. Patch GAN由于不包含FC层,D和G都可应用与任何大小的图片。(Figure 8)中的G在train阶段使用256x256图片,在test阶段使用512x512图片。

- Perceptual validation
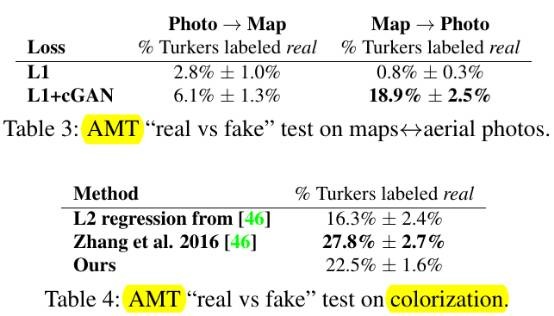
- Semantic segmentation
GAN一般用于图像生成,本论文尝试将cGAN用于做segmentation任务,但最终效果并不好。(Figure 10, Table 5)从实验结果可以看出, reconstruction losses like L1 are mostly sufficient.

- Semantic labels↔photo
Cityscapes dataset

- Architectural labels→photo
CMP Facades dataset

- Map↔aerial photo
Google Maps

- BW→color photos

- Edges→photonary
- Sketch→photo

- Day→night

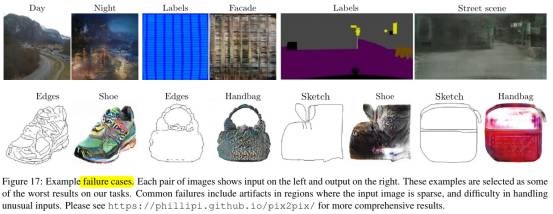
- Failure case